URL Encoding
URLs can only be sent over the internet using the ASCII character-set. URL encoding (also known as percent encoding) converts characters into a format that can be sent over the Internet, using a % followed by two hexadecimal digits. This ensures that URLs are properly formatted and can be interpreted correctly by web services.
For URLs, there are many reserved and common special characters:
-
Reserved Characters: Characters with special meanings or functions in URLs are reserved. These include
!,*,',(,),;,:,@,&,=,$,,,/,?,#,[,], and more. -
Unsafe Characters: Other characters outside of the ASCII character-set must be encoded, such as,
",\<,>,\,\{,},|,^,~,[,],`. -
Handling spaces: URLs cannot contain spaces. When encoding whitespace characters you have two options:
-
Using
%20(percent encoding); or -
Using
+(for building query strings).
-
How to URL Encode in IguanaX:
Method 1: net.http.get parameters argument automatically formats the query string
When using net.http.get{}, the parameters argument takes in a table of key-value pairs and automatically formats the query string. The url can also be hardcoded to handle query parameters if desired.

Here the request URL would be formatted as follows:
https://api.example.com/patient?name=John%20Doe
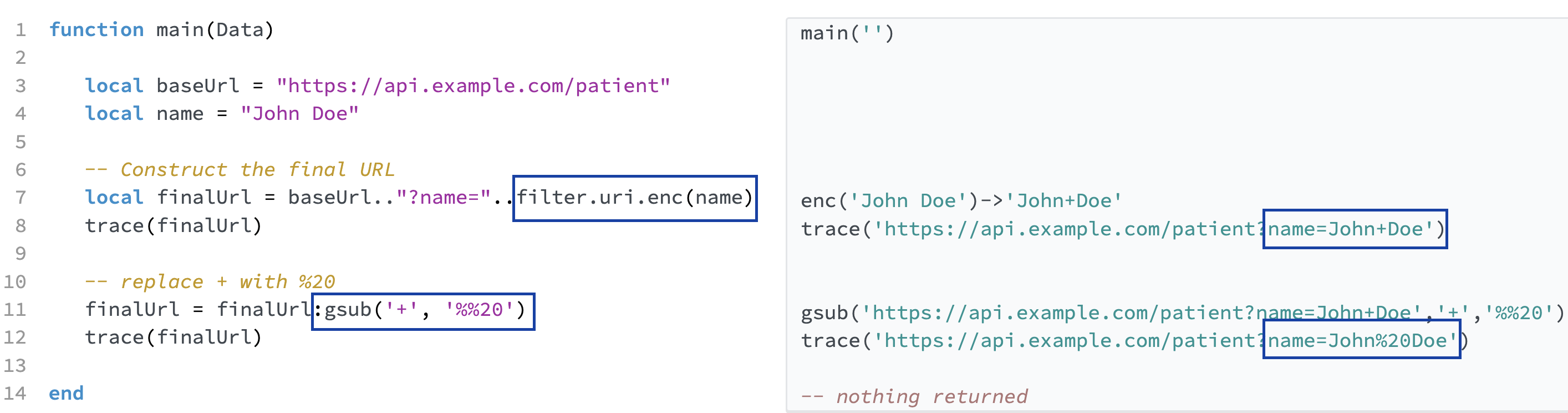
Method 2: filter.uri.enc and string:gsub can be used to conver
filter.uri.enc() can be used to URL encode strings with reserved and special characters in Iguana's Translator.
filter.uri.enc() will convert <spaces> to +. String:gsub() can be used to replace the + with %20 when required.