Parsing and Serializing JSON
Working with JSON data in Iguana is easy. You can parse, create, and serialize JSON data efficiently using the built-in json module. Below is a quick guide on how to manage JSON data in the Translator.
Parsing JSON:
To parse incoming JSON data, use the json.parse{} function. This will convert a JSON string into a Lua table, which can then be manipulated easily.
Parse JSON strings into a Lua table
Try it out with this simple code snippet:
local jsonTemplate = [[
{
"firstname":"John",
"lastname":"Doe",
"birthdate":"1997-04-11",
"phone":"(905)343-2352"
}
]]
function main(Data)
-- parse JSON
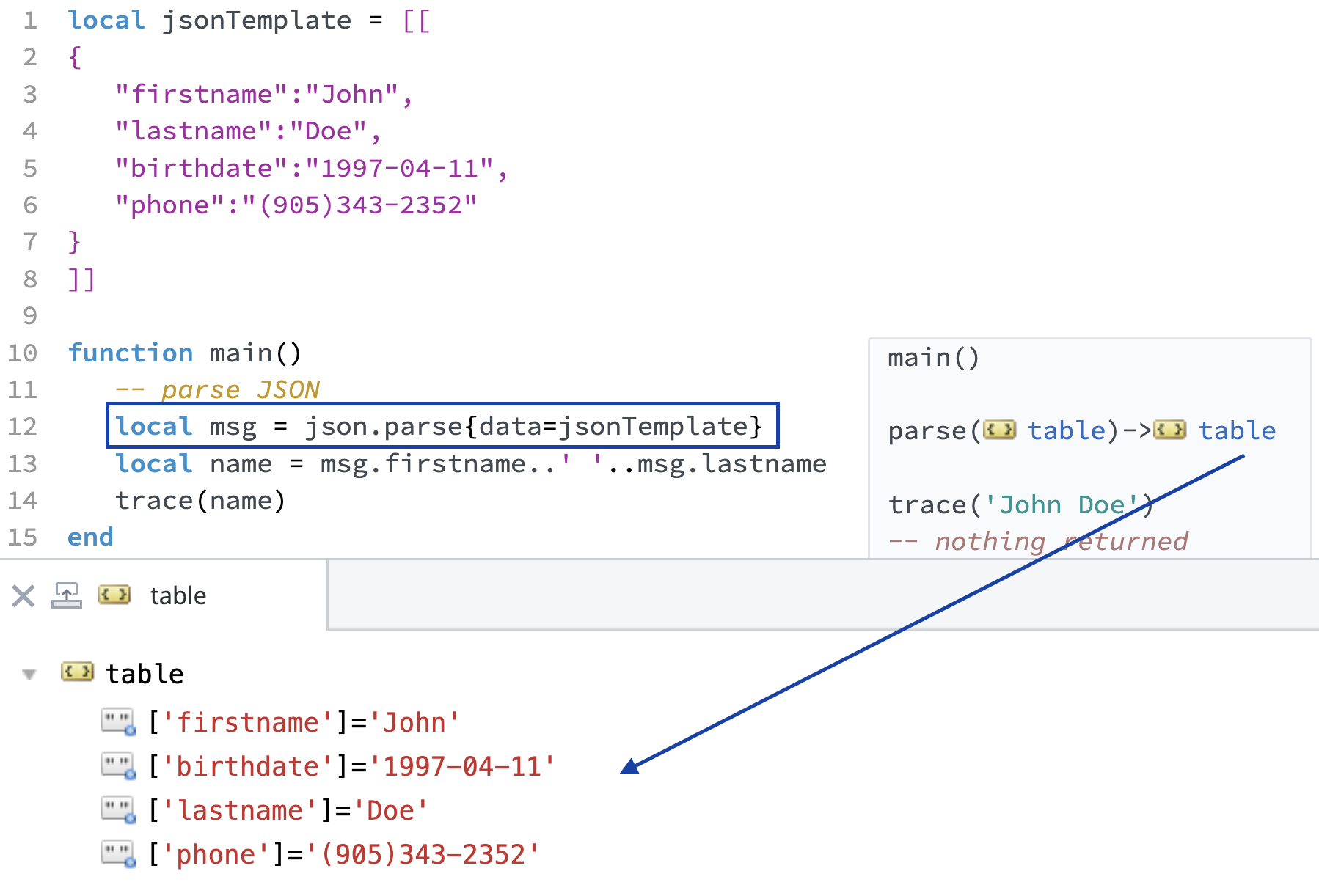
local msg = json.parse{data=jsonTemplate}
local name = msg.firstname..' '..msg.lastname
trace(name)
end
Use the annotations to view the lua table generated from the JSON string.
Generating and Serializing JSON:
To generate JSON, use json.serialize{} to serialize Lua tables into a JSON Object or Array.
STEP 1: Generate a Lua Table
First, you can create a Lua table, either by following a static template or dynamically based on available inbound data from a source system.
For example, take this sample HL7 message and use it as sample data to map to a lua table. For practice, create a simple VMD called adt.vmd file and import the ADT^A04 for HL7v2.3.
MSH|^~\&|SENDING_APP|SENDING_FACILITY|RECEIVING_APP|RECEIVING_FACILITY|20110613083617||ADT^A04|934576120|P|2.3||||
EVN|A04|20110613083617|||
PID|1||135769||Mouse^Mickey||19281118|M|||123 Main St.^^Lake Buena Vista^FL^32830||(407)939-1289|||||1719|99999999|||
PV1|1|O|||||7^Disney^Walt^^MD^^^^||
-
Using a Predefined Template:
Typically, the JSON template values will start as empty strings or JSON NULLs, ready to be populated.
local jsonTemplate = [[
{
"firstname":"",
"lastname":"",
"birthdate":"",
"phone":""
}
]]
function main(Data)
-- parse JSON
local msg = json.parse{data=jsonTemplate}
-- map HL7 to Lua table
local msgIn = hl7.parse{vmd='adt.vmd', data=Data}
msg.firstname = msgIn.PID[5][2]:nodeValue()
msg.lastname = msgIn.PID[5][1]:nodeValue()
msg.birthdate = msgIn.PID[7]:nodeValue()
msg.phone = msgIn.PID[13][1]:nodeValue()
end
-
Dynamic Generation:
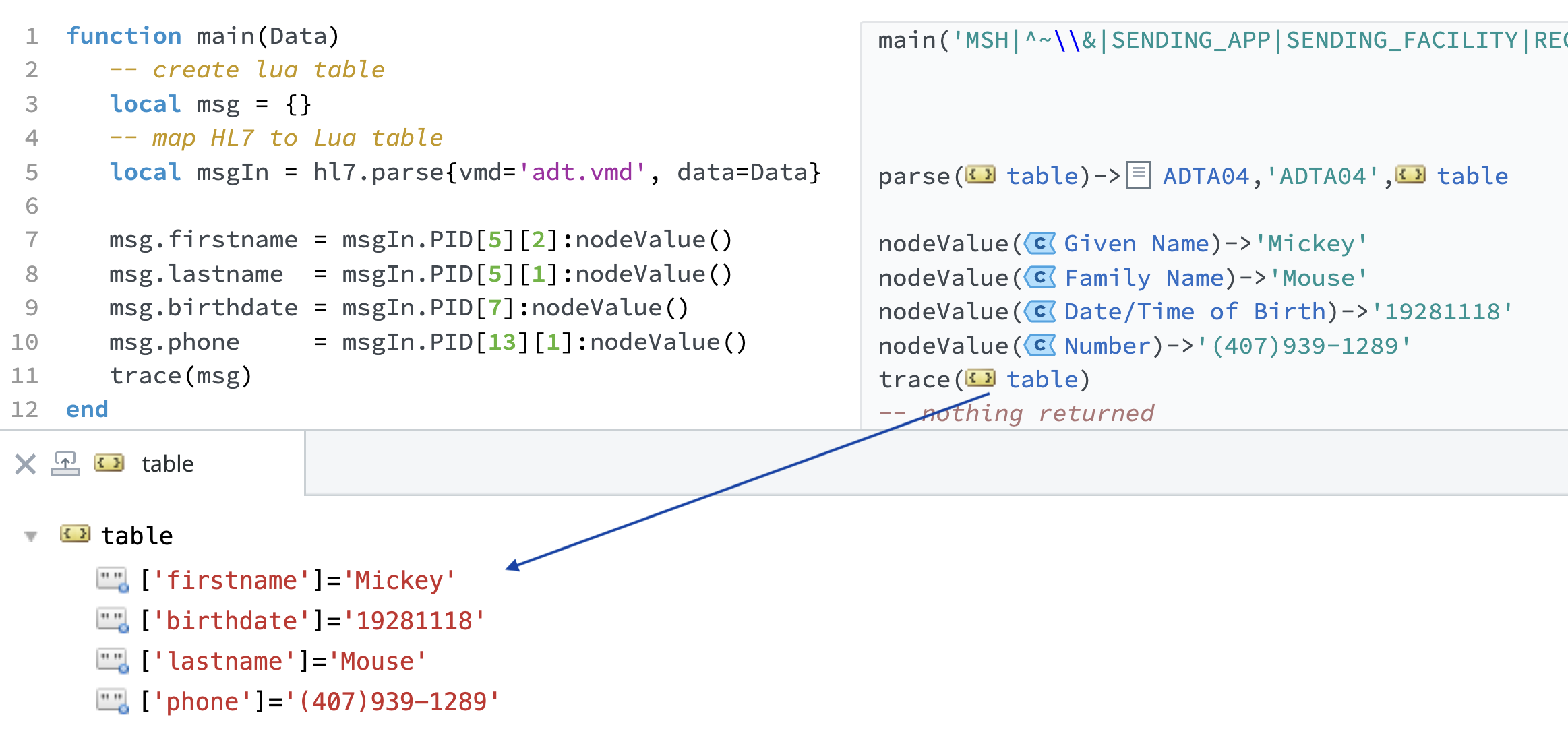
function main(Data)
-- create lua table
local msg = {}
-- map HL7 to Lua table
local msgIn = hl7.parse{vmd='adt.vmd', data=Data}
msg.firstname = msgIn.PID[5][2]:nodeValue()
msg.lastname = msgIn.PID[5][1]:nodeValue()
msg.birthdate = msgIn.PID[7]:nodeValue()
msg.phone = msgIn.PID[13][1]:nodeValue()
end
Both methods will result in the same Lua table:
STEP 2: Serialize the Lua table to a JSON string
Once you've built or modified your Lua table, you can serialize it back into JSON format using the json.serialize{} function.
This is useful when you need to send the data to an external service or log it in JSON format.
local jsonString = json.serialize{data=msg}
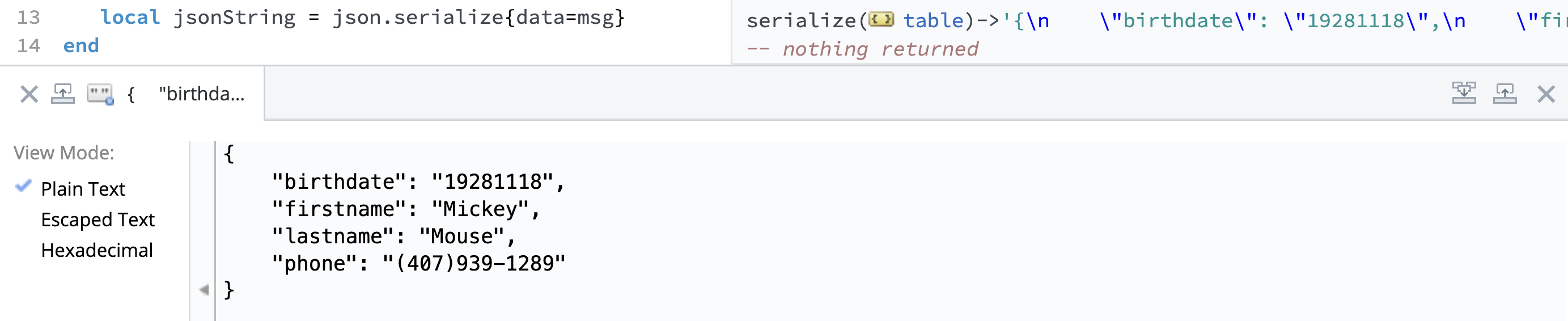
You can also use The string viewing window to view this json string in different view modes.