IguanaX HA Cloud Solutions
Overview
This document describes how IguanaX High Availability (HA) can be implemented in public cloud environments using a simple Active-Passive HA architecture.
The goal is to help customers understand:
-
How IguanaX HA concepts map to cloud infrastructure
-
Which cloud-native services are typically involved
-
How failover and recovery behave in a cloud environment
This document is conceptual, not a step-by-step deployment guide.
Active-Passive HA in the Cloud
The following diagram illustrates a reference Active-Passive IguanaX HA deployment that applies to both AWS and Azure.
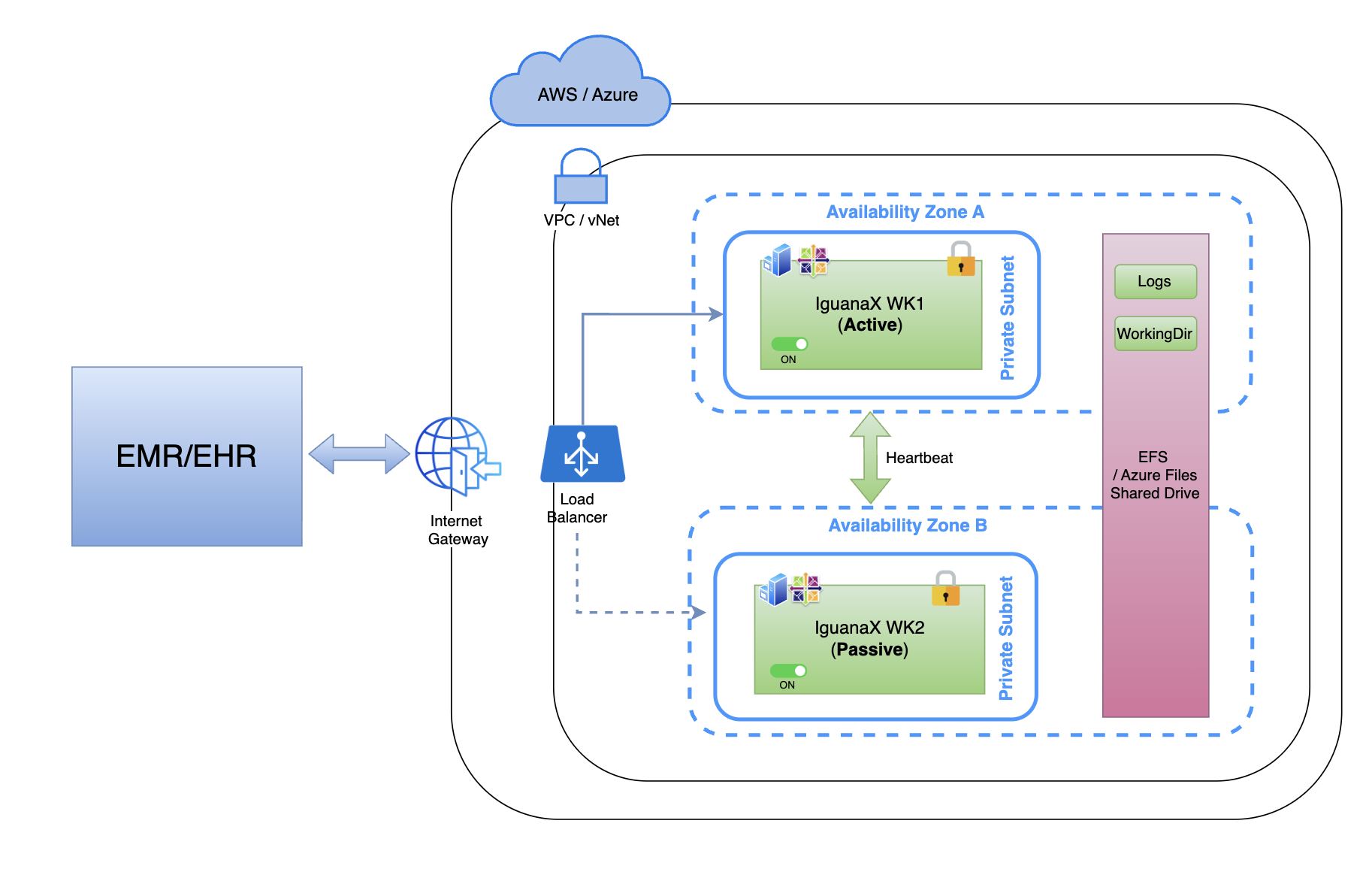
Key Components:
-
A single cloud region (AWS or Azure)
-
Two availability zones
-
One Active IguanaX instance
-
One Passive IguanaX instance
-
A shared cloud file system for logs and queues
-
A cloud-native load balancer handling inbound traffic
Although AWS and Azure use different service names, the HA behavior and guarantees are the same.
Cloud Architecture Review
Network Boundary
-
All components reside within a single VPC (AWS) or vNet (Azure)
-
Access is controlled using cloud-native security constructs
-
Inbound traffic enters through:
-
Internet Gateway (or equivalent)
-
Cloud Load Balancer
-
Load Balancer
The load balancer sits in front of IguanaX and is responsible for:
-
Receiving inbound LLP and HTTP(S) traffic
-
Performing health checks on IguanaX instances
-
Routing traffic only to the Active IguanaX instance
The load balancer does not manage message recovery or sequencing—it only controls traffic routing.
IguanaX Application Layer
Availability Zone A - Active IguanaX
-
Runs the Active IguanaX instance
-
Processes all inbound messages
-
Writes logs and queue data to shared storage
-
Communicates with the Passive instance via heartbeat
Availability Zone B - Passive IguanaX
-
Runs a Passive (hot-standby) IguanaX instance
-
Remains ON and fully initialized
-
Continuously monitors the Active instance
-
Has access to the same shared logs and queues
At any time, only one IguanaX instance is Active.
Shared Storage (EFS / Azure Files)
A shared file system is used to store:
-
Message queues
-
IguanaX logs
-
Shared WorkingDir content required for recovery
Cloud Platform | Shared Storage Service |
|---|---|
AWS | Amazon EFS |
Azure | Azure Files |
This shared storage is the key enabler for:
-
Queue recovery
-
Message sequencing
-
Seamless failover
AWS and Azure: Same Model, Different Services
Although AWS and Azure use different terminology, the HA model remains the same.
Concept | AWS | Azure |
|---|---|---|
Compute | EC2 | Virtual Machines |
Load Balancer | ALB / NLB | Azure Load Balancer |
Shared Storage | EFS | Azure Files |
Network | VPC | vNet |
Availability Boundary | Availability Zones | Availability Zones |
Customers should choose services based on platform familiarity and performance requirements, not HA behavior differences.
What This Cloud HA Design Guarantees
-
Automatic failover within a region
-
Continuous availability of LLP and HTTP endpoints
-
Queue recovery and message sequencing
-
No single point of failure at the VM level
What This Cloud HA Design Does Not Guarantee
-
Zero downtime during failover
-
Cross-region disaster recovery
-
Protection from application-level configuration errors
Cloud HA improves availability within a region, not across regions.
HA vs Cloud Disaster Recovery
This architecture is designed for High Availability, not Disaster Recovery.
-
HA protects against instance or zone failures
-
DR protects against region-wide outages
Combining HA and DR into a single design (for example, spanning regions) is not recommended due to:
-
High latency
-
Complex global load balancing
-
Expensive cross-region storage replication
HA and DR should be designed separately.
Getting Started
This document provides a conceptual reference for IguanaX Active-Passive HA in the cloud.
To design, validate, and deploy an IguanaX HA solution in AWS or Azure:
-
Contact your Interfaceware account manager, or
-
Email the Interfaceware Support Team at support@interfaceware.com
Our team can help you:
-
Validate cloud architecture
-
Size storage and compute correctly
-
Review HA assumptions and guarantees
-
Plan failover testing