Cloud - GitLab Setup
Follow the steps below to configure your IguanaX Git settings with GitLab cloud service.
In IguanaX, go to Settings > Git. For each step, click on the  button to set your configurations.
button to set your configurations.
STEP 1: Author Info - Enter a name and email to be used to label your commits
Git requires a name and email to label your commits. We recommend you use an email address recognized by your GitLab so you can trace your commits in it.
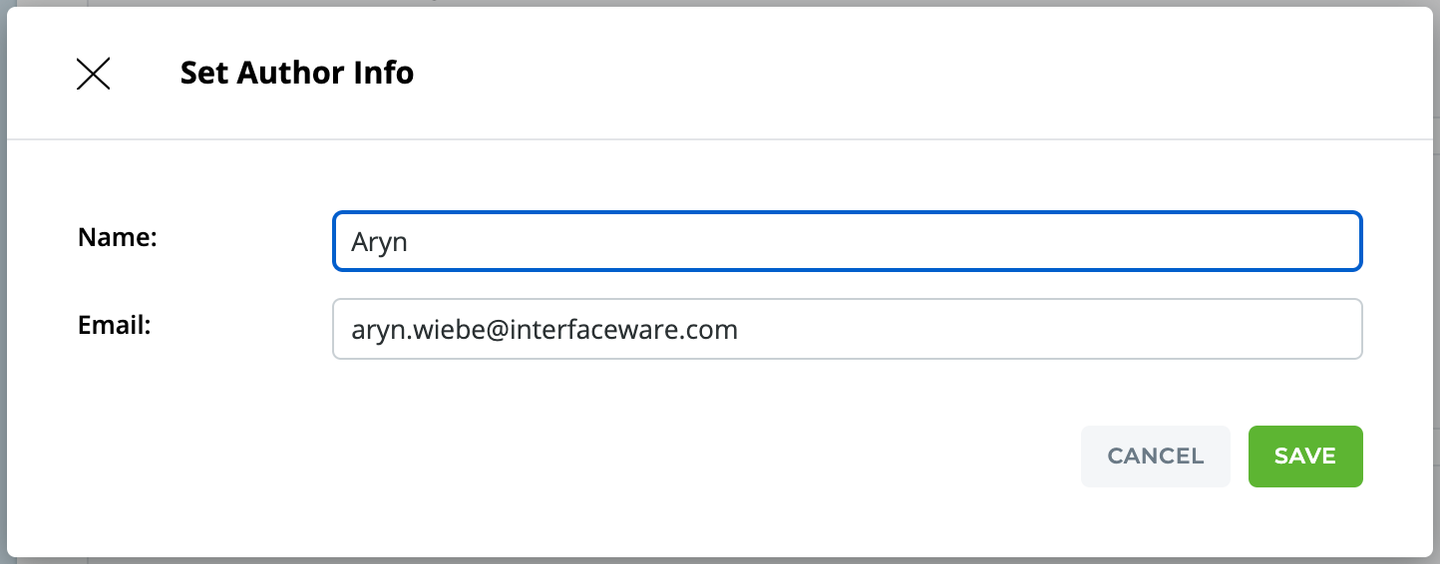
We also use this Author Info to help Identify your Iguana so if you have problems we can help you!
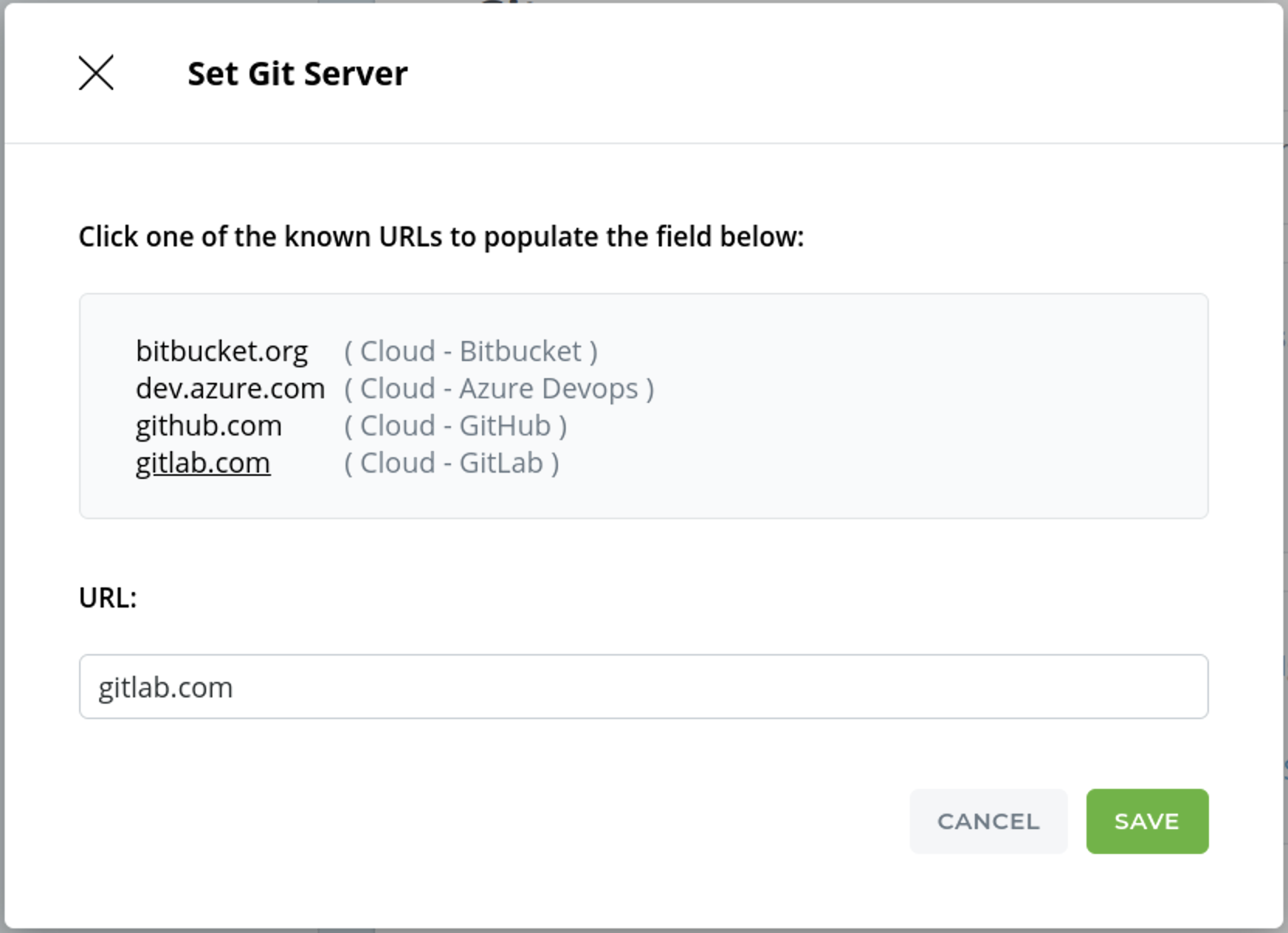
STEP 2: Git Server - Choose gitlab.com
Select gitlab.com (Cloud - GitLab) from the list of Git Servers. Click Save.
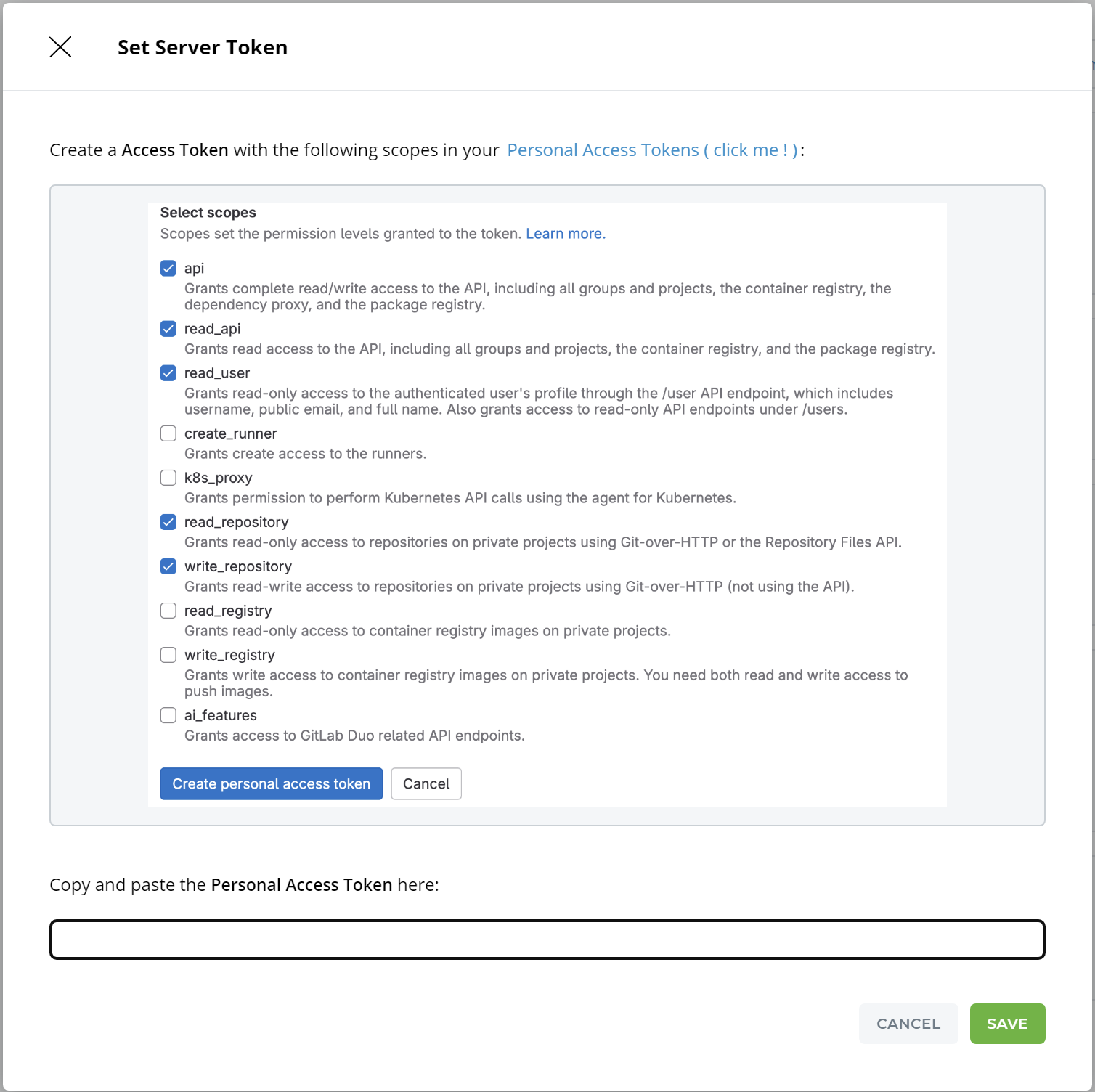
STEP 3: Server Token - In GitLab, generate a personal access token for the User to authenticate
IguanaX needs to have the ability to create Git repositories on GitLab. This means we need to create an access token with the correct permissions. Iguana will use the token to authenticate with GitLab.
-
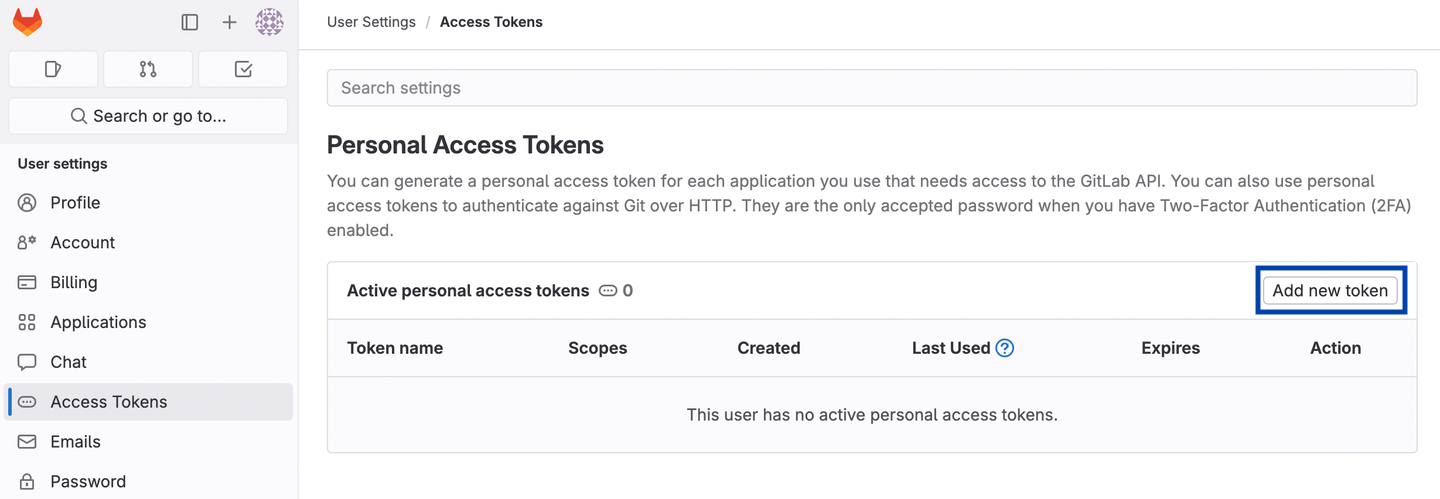
Go to https://gitlab.com/-/user_settings/personal_access_tokens to create a new access token in GitLab.
-
Click Add new token
-
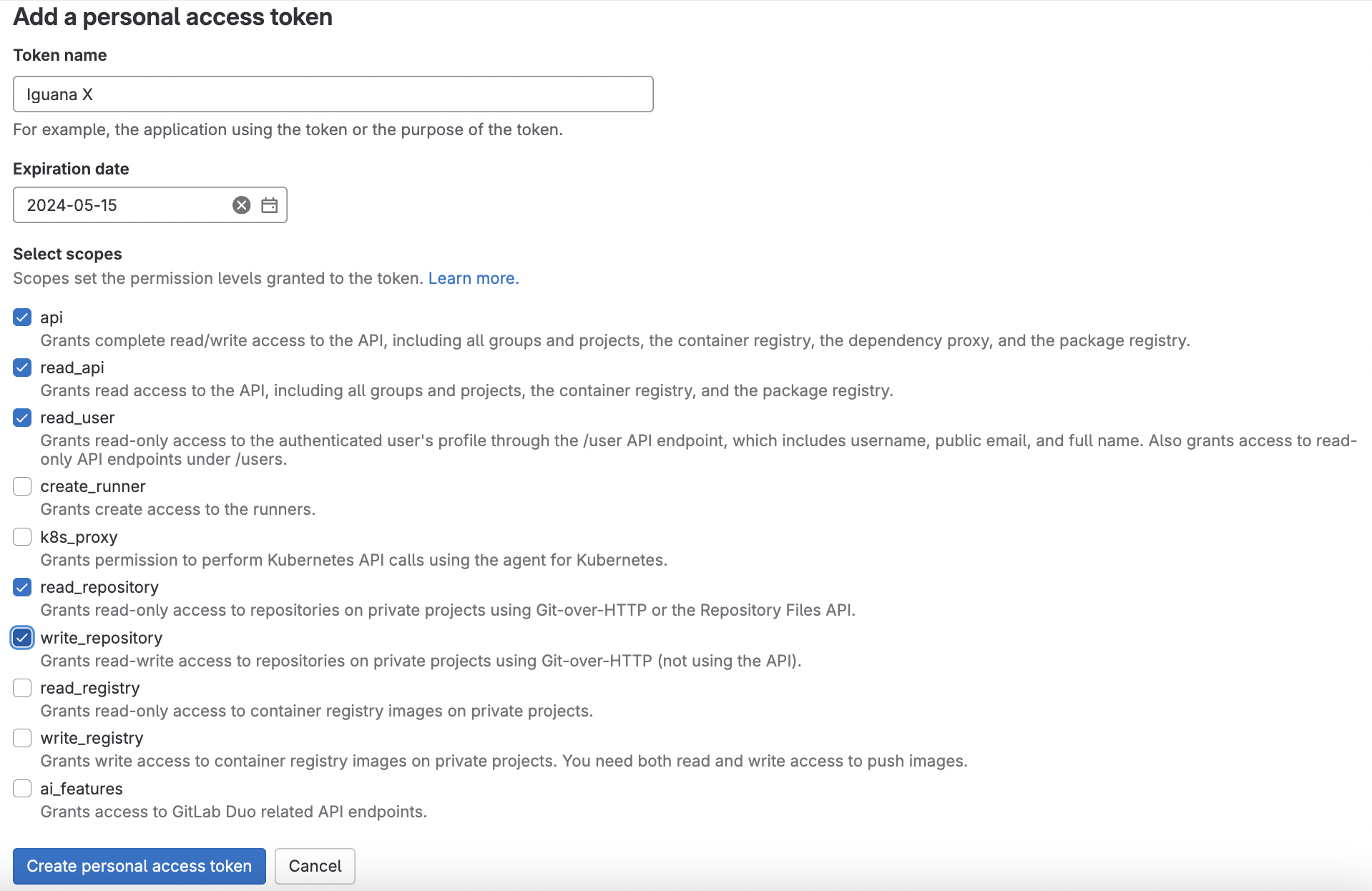
Enter a Token Name, Expiration Date and grant the following Scopes. Click Create Personal Access Token:
-
Copy the generated GitLab access token and paste it in your IguanaX Git Server Token setting and click Save. GitLab will only show you this once - if you forget it you will need to generate a fresh one.
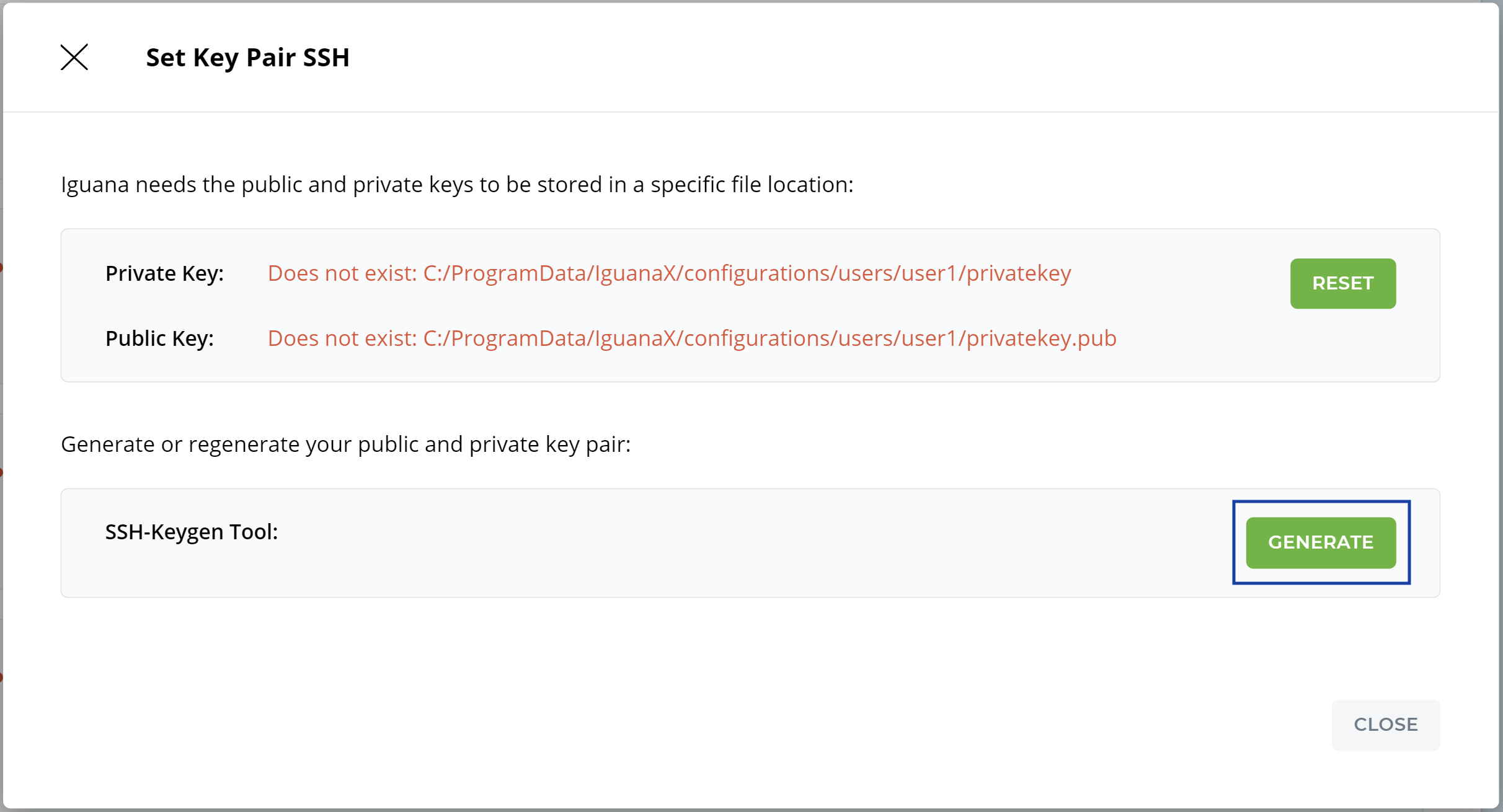
STEP 4: Key Pair SSH - Generate a public-private key pair for SSH authentication with GitLab
In Key Pair SSH window, use the Generate button to have Iguana generate a private key pair for you. For more information on SSH see: How does IguanaX use SSH?
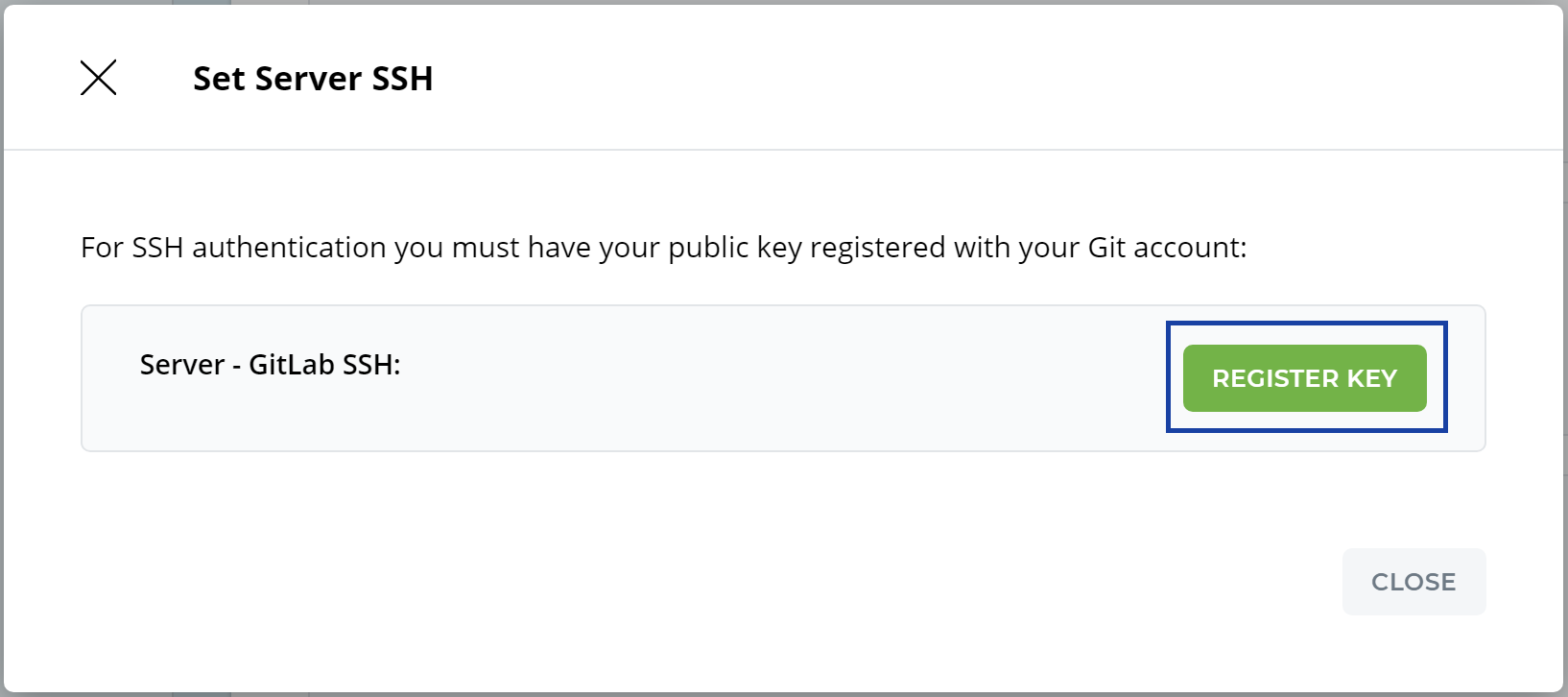
STEP 5: Server SSH - Register your public key with your cloud host
In Server SSH, click Register to have Iguana register your public key with GitLab.
You can see the registered public key in GitLab User Settings > SSH Keys.